Results
-
HD Quiz powered by harmonic design
#1. What speed is required to achieve maximum endurance in a piston engine powered and jet engine powered aircraft respectively?
#2. Select the appropriate words to complete the following statement. Fuel flow in a piston engine aircraft is proportional to .......... whilst that in a jet powered aircraft is proportional to ......... Thrust output of a jet engine .................. with increasing airspeed whilst that of a piston engine ................ 1. Is approximately constant 2. Thrust 3. Reduces rapidly 4. Power 5. RPM
#3. Select the correct words to complete the following statement. To achieve the maximum possible glide range it is necessary to fly at ........... This is achieved by flying the aircraft in a .................... condition and at .........?
#4. What speed is required to achieve maximum angle of climb in a jet aircraft and a piston aircraft respectively and for what purpose might this be required?
#5. What is the effect of increasing altitude on best rate of climb IAS and best climb TAS respectively?
#6. What happens to the range between minimum and maximum flight speeds for a subsonic aircraft as altitude increases?
#7. Select the appropriate words to complete the following statement. Thrust horsepower output of a propeller aircraft ...... with increasing airspeed whilst that of a jet ... 1. Is approximately constant. 2. Is unchanged. 3. Increases rapidly then decreases rapidly. 4. Reduces slowly. 5. increases approximately linearly.
#8. When flying at VMD an aircraft has a C1, of 0.45 and a CD of 0.0225. If its engines fail when flying at 36000 feet what will be its maximum glide range?
#9. When flying at VMD an aircraft weighing 400000 Ibf has a CL of 0.45 and a CD of 0.0225. If its engines fail when flying at 36000 feet what will be its maximum glide range if the pilot immediately dumps 100000 lbf of fuel? What effect will the reduced weight have on VMD?
#10. What is the available rate of climb at service ceiling for a piston and jet aircraft respectively?
#11. What speed is required to achieve best rate of climb in a piston and jet aircraft respectively?
#12. How is the absolute ceiling indicated on a power available / power required graph for a piston and jet aircraft respectively?
#13. What will be the effect of a headwind on glide range and glide angle respectively?
#14. What will be the effect of a tailwind on glide range and rate of descent?
#15. Which of the following best describes the effect of flap deployment?
#16. Best endurance for a piston aircraft is achieved at VMP, whilst that for a jet aircraft is achieved at (VMD) Why is this so?
#17. Which of the following best describes the effect of increasing altitude on maximum rate of climb?
#18. Which of the following best describes the manner in which best climb speed varies with altitude?
#19. How will a headwind and a tailwind respectively affect best range glide speed?
#20. If an aircraft enters a banked turn whilst climbing to cruising altitude what effect will this have on rate of climb at constant power setting?
#21. Select the appropriate words to complete the following statement. Fuel flow in a piston engine aircraft is proportional to .......... whilst that in a jet powered aircraft is directly proportional to ......... Thrust available from a jet engine .................. with increasing airspeed whilst that of a piston engine ................ 1. Is approximately constant 2. Thrust 3. Reduces rapidly 4. Power 5. Increases approximately linearly
#22. An aircraft weighing 200000 Ibf has a maximum excess power available of 1500 Thrust Horse Power. What will be its maximum rate of climb?
#23. An aircraft weighing 50000 lbf requires a thrust of 20000 Ibf when flying straight and level at 250 Kts IAS. What will be its maximum angle of climb at this speed assuming its maximum thrust at this speed is 40000 lbf and the total drag force does not change during the climb?
#24. In tlie climb described in question 23 what will be the lift force generated by the aircraft?
#25. An aircraft weighing 50000 Ibf requires a thrust of 20000 Ibf when flying straight and level at 250 Kts IAS. How many Thrust Horse Power will it be developing when flying straight and level at this speed? (Assume 1 nm = 6000 ft)
#26. Which of the following describes the method of calculating the thrust horsk power being developed by an aircraft in unaccelerated straight and level flight? 1. Convert EAS into feet per minute, multiply by total drag in Ibf then divide by 33000 ft lbflmin. 2. Convert TAS into feet per second, multiply by total drag in Ibf then divide by 550 ft Ibflsec. 3. Convert EAS into feet per second, multiply by total drag in Ibf then divide by 550 ft Ibflsec. 4. Convert TAS into feet per minute, multiply by total drag in Ibf then divide by 33000 ft Ibf lmin.
#27. An aircraft weighing 50000 Ibf requires a thrust of 20000 Ibf when flying straight and level at 250 Kts IAS. If it were to climb to 40000 ft what would be its power available in comparison to that at ISA msl?
#28. What would be the effect of sweeping back the wings of a variable geometry aircraft in gliding flight?
#29. How is maximum rate of emergency descent achieved in a high speed jet aircraft?
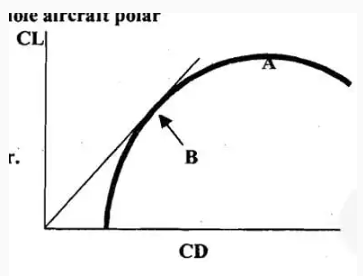
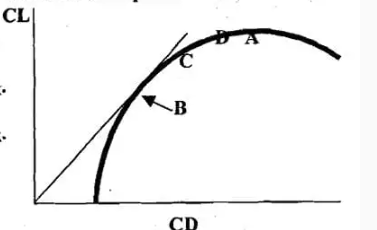
#30. What do points A and B represent on the whole aircraft polar diagram right?
#31. An aircraft weighing 50000 Ibf is able to achieve a maximum rate of climb of 1500 ft / min when climbing at 250 Kts TAS. How much Excess Power will be required to achieve this rate of climb?
#32. An aircraft weighing 50000 Ibf is able to achieve a maximum rate of climb of 1500 ft / min when climbing at 250 Kts TAS. What will be the maximum all up weight at which it can achieve a 5% climb gradient at this speed assuming its power available and total drag do not change during the climb?
#33. Increased weight reduces the rate of climb and climb gradient but?
#34. Best climb gradient is achieved by flying at approximately?
#35. Absolute ceiling occurs when?
#36. What airspeed will produces the greatest glide endurance?
#37. What factors determine maximum glide range?
#38. What are VMCAa nd VMDR?
#39. How do VMGA and VMDR compare?
#40. Which of the following is equal to lift in a steady climb or descent?
#41. What proportion of thrust is employed in supporting the weight of an aircraft in a steady climb?
#42. What provides maximum glide range?
#43. What would give maximum glide range in a headwind?
#44. What would give maximum glide range in a tailwind?

#45. Which of the points on the CL:CD polar would give maximum glide range?
#46. In a steady climb?
#47. What is the speed for minimum sink rate?
#48. What flap position would give maximum glide range?
#49. What speed gives best angle of climb in a jet aircraft?
#50. Which of the following occur at VMD? 1. L:D Max. 2. Max jet endurance. 3. ax prop range. 4. Max jet climb angle. 5. Max glide range all types.
#51. What will be the effect of an increase in weight? 1. VMD will increase. 2. Glide range will decrease. 3. Glide angle will increase. 4. Glide range and angle will be unaffected.
#52. In what direction does lift act in a steady climb?
#53. What is the absolute ceiling of an aircraft? 1. The altitude where the low speed and high speed stall lines cross. 2. The altitude at which power required is equal to power available. 3. The altitude at which thrust available is equal to drag. 4. The altitude at which rate of climb is zero.
#54. Increasing aircraft weight. .. .... . ..glide speed and... .... rate of descent?
#55. To descend at constant glide angle and IAS, the pitch attitude must.. .. .......?
#56. For a constant mach number descent, gradient must ...... ?
#57. For a constant IAS descent, gradient must ...... ?
#58. A headwind in a constant mach number climb will ............ angle of climb?
#59. For maximum glide range, TAS must ..... ?
#60. To descend at constant IAS the ............m ust be ..........?
#61. Best cHtnb angle is achieved at.............. ?
#62. Maximum rate of climb occurs at ........... speed?
#63. Maximum glide range is achieved at. ...........?
#64. Load factor in a steady climb will be.... ... ?
#65. Lift in a steady climb is equal to ........ ?
#66. The correct procedure for an emergency descent is?
#67. Which of the following is correct for a jet aircraft?
#68. Rate of climb is .......... by a headwind?
#69. Angle of climb is .......... by a headwind?
#70. Climb gradient is ........ try a headwind?
#71. Power required is .......... as altitude increases in a steady climb?
#72. Load factor is ....... in a steady climb?
#73. If excess power is 25000 ft Ibflmin and aircraft weight is 10000 Ibf what will be the maximum rate of climb?
#74. If maximum thrust is 25000 Ibf, drag is 15000 Ibf and weight is 10000 Ibf what will be the maximum angle of climb?
#75. If at 250 Kts, excess power is 50,000,000 ft Ibflmin, and weight is 10000 Ibf, what is maximum angle of climb?
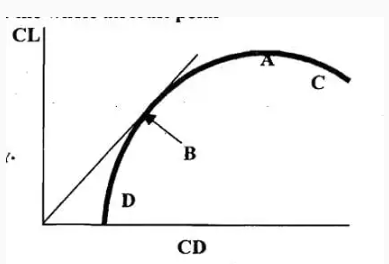
#76. What might the points C and D represent on the whole aircraft polar Diagram right?