Results
-
HD Quiz powered by harmonic design
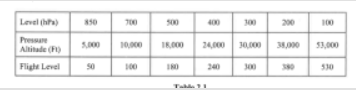
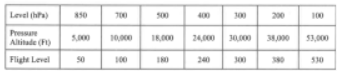
#1. The 850 hPa pressure level can vary in height. In temperate regions which of the following average heights is applicable?
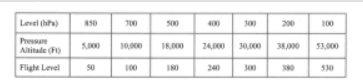
#2. Which constant pressure altitude chart is standard for 18,289 FT pressure level (FL 180)?
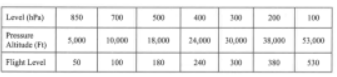
#3. If you are planning a flight at FL 170, which of these upper wind and temperature charts would be nearest your flight level?