Results
-
HD Quiz powered by harmonic design
#1. What % of CL max would a wing produce when flying at 1.3 Vs?
#2. What is the relationship in straight and level flight between the CL at any given speed and CL Max?
#3. If the C of G is moved forward what will be the effect on stalling speed?
#4. If the C of G of an aircraft is moved forward what will be the effect on longitudinal, directional and lateral stability?
#5. If the C of G is moved forward what will be the effect on longitudinal, directional and lateral manoeuvrability.
#6. If the weight of an aircraft is doubled what will be the effect on its stalling speed?
#7. A JAR certificated commercial passenger aircraft is flying in straight and level flight when the stall warning system activates the stick shaker. What will be its CL as a percentage of CL Max?
#8. Which of the following statements are true of an aircraft as it climbs to high altitude at constant IAS?
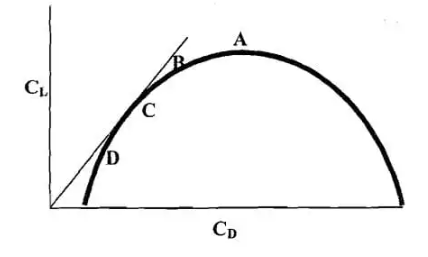
#9. The sketch below represents a typical whole aircraft L:D polar diagram. Which of the points marked on it correspond to the low speed stall condition?